Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Plotting with Configurations in pyprocar#
This example illustrates how to utilize various configurations for plotting the 3D Fermi surface using the pyprocar package. It provides a structured way to explore and demonstrate different configurations for the plot_fermi_surface function.
Symmetry does not currently work! Make sure for Fermi surface calculations to turn off symmetry.
Preparation#
Before diving into plotting, we need to download the example files. Use the following code to do this. Once downloaded, specify the data_dir to point to the location of the downloaded data.
Downloading example#
data_dir = pyprocar.download_example(save_dir='',
material='Fe',
code='vasp',
spin_calc_type='non-spin-polarized',
calc_type='fermi')
import pyvista
# You do not need this. This is to ensure an image is rendered off screen when generating example gallery.
pyvista.OFF_SCREEN = True
import os
import pyprocar
data_dir = os.path.join(
pyprocar.utils.DATA_DIR, "examples", "Fe", "vasp", "non-spin-polarized", "fermi"
)
# First create the FermiHandler object, this loads the data into memory. Then you can call class methods to plot.
# Symmetry only works for specific space groups currently.
# For the actual calculations turn off symmetry and set 'apply_symmetry'=False.
fermiHandler = pyprocar.FermiHandler(code="vasp", dirname=data_dir, apply_symmetry=True)
WARNING : Fermi Energy not set! Set `fermi={value}`. By default, using fermi energy found in given directory.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
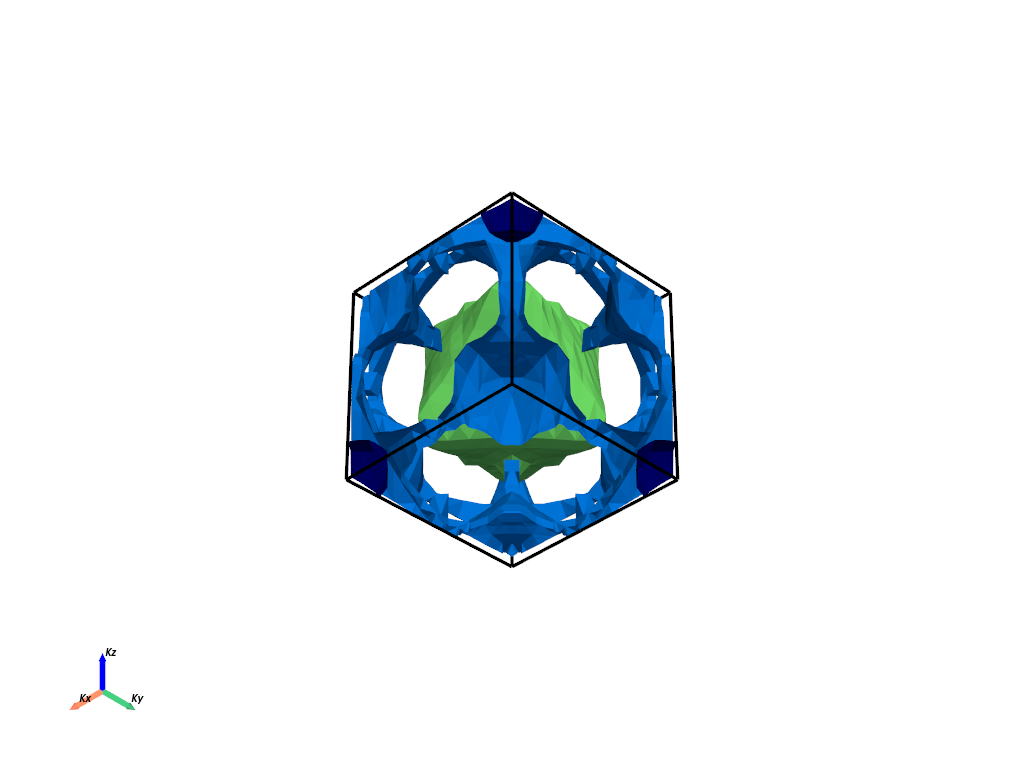
# Section 1: Plain Mode
# ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
#
# This section demonstrates how to plot the 3D Fermi surface using default settings.
# Section 1: Locating and Printing Configuration Files
# ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
#
# This section demonstrates where the configuration files are located in the package.
# It also shows how to print the configurations by setting print_plot_opts=True.
#
# Path to the configuration files in the package
config_path = os.path.join(pyprocar.__path__[0], "cfg")
print(f"Configuration files are located at: {config_path}")
fermiHandler.plot_fermi_surface(mode="plain", show=True, print_plot_opts=True)
Configuration files are located at: C:\Users\lllang\Desktop\Current_Projects\pyprocar\pyprocar\cfg
--------------------------------------------------------
There are additional plot options that are defined in a configuration file.
You can change these configurations by passing the keyword argument to the function
To print a list of plot options set print_plot_opts=True
Here is a list modes : plain , parametric , spin_texture , overlay
Here is a list of properties: fermi_speed , fermi_velocity , harmonic_effective_mass
--------------------------------------------------------
plot_type: PlotType.FERMI_SURFACE_3D
custom_settings: {}
mode: plain
property: FermiSurfaceProperty.FERMI_SPEED
background_color: white
plotter_offscreen: False
plotter_camera_pos: [1, 1, 1]
surface_cmap: jet
surface_color: None
surface_opacity: 1.0
surface_clim: None
surface_bands_colors: []
spin_colors: (None, None)
arrow_size: 3
texture_cmap: jet
texture_color: None
texture_size: 0.1
texture_scale: False
texture_opacity: 1.0
brillouin_zone_style: wireframe
brillouin_zone_line_width: 3.5
brillouin_zone_color: black
brillouin_zone_opacity: 1.0
add_axes: True
x_axes_label: Kx
y_axes_label: Ky
z_axes_label: Kz
axes_label_color: black
axes_line_width: 6
add_scalar_bar: True
scalar_bar_labels: 6
scalar_bar_italic: False
scalar_bar_bold: False
scalar_bar_title: None
scalar_bar_title_font_size: None
scalar_bar_label_font_size: None
scalar_bar_position_x: 0.4
scalar_bar_position_y: 0.01
scalar_bar_color: black
property_name: fermi_speed
fermi_tolerance: 0.1
extended_zone_directions: None
supercell: [1, 1, 1]
projection_accuracy: high
interpolation_factor: 1
max_distance: 0.3
cross_section_slice_linewidth: 5.0
cross_section_slice_show_area: False
isoslider_title: Energy iso-value
isoslider_style: modern
isoslider_color: black
orbit_gif_n_points: 36
orbit_gif_step: 0.05
orbit_mp4_n_points: 36
orbit_mp4_step: 0.05
ij,uvwabj->uvwabi
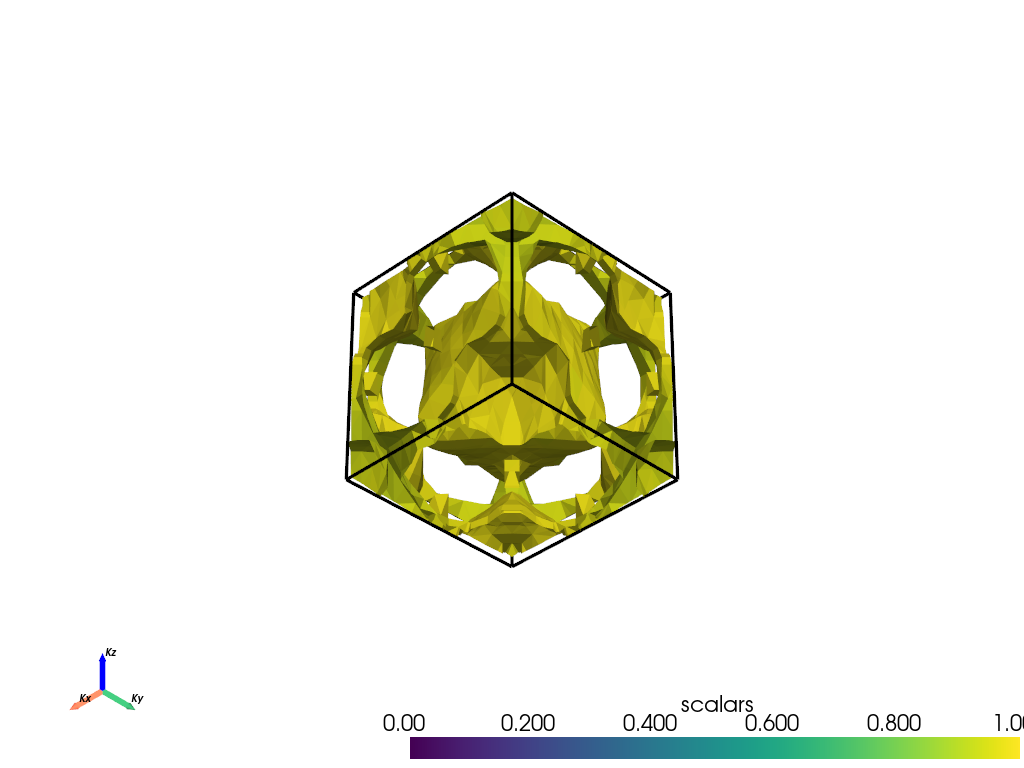
# Section 2: Parametric Mode with Custom Settings
# ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
#
# This section demonstrates how to customize the appearance of the 3D Fermi surface in parametric mode.
# We'll adjust the colormap, color limits, and other settings.
atoms = [0]
orbitals = [4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
spins = [0]
fermiHandler.plot_fermi_surface(
mode="parametric",
atoms=atoms,
orbitals=orbitals,
spins=spins,
surface_cmap="viridis",
surface_clim=[0, 1],
show=True,
)
--------------------------------------------------------
There are additional plot options that are defined in a configuration file.
You can change these configurations by passing the keyword argument to the function
To print a list of plot options set print_plot_opts=True
Here is a list modes : plain , parametric , spin_texture , overlay
Here is a list of properties: fermi_speed , fermi_velocity , harmonic_effective_mass
--------------------------------------------------------
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.564 seconds)