Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Example of finding the bandgap#
The ElectronicBandStructure is used to handle the information related to the electronic band structure.
General Format#
import pyprocar
pyprocar.io.Parser(code="vasp", dir=data_dir)
Downloading example#
data_dir = pyprocar.download_example(save_dir='',
material='Fe',
code='vasp',
spin_calc_type='non-spin-polarized',
calc_type='bands')
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 1
import pyvista as pv
# You do not need this. This is to ensure an image is rendered off screen when generating exmaple gallery.
pv.OFF_SCREEN = True
importing pyprocar and specify the local data_dir
import os
import numpy as np
import pyprocar
data_dir = os.path.join(
pyprocar.utils.DATA_DIR, "examples", "Fe", "vasp", "non-spin-polarized", "fermi"
)
Initialize the parser object and get the ElectronicBandStructure
parser = pyprocar.io.Parser(code="vasp", dir=data_dir)
ebs = parser.ebs
e_fermi = parser.ebs.efermi
structure = parser.structure
# Apply symmetry to get a full kmesh
if structure.rotations is not None:
ebs.ibz2fbz(structure.rotations)
You can print the object to see some information about the Band Structure
print(ebs)
Enectronic Band Structure
------------------------
Total number of kpoints = 3375
Total number of bands = 8
Total number of atoms = 1
Total number of orbitals = 9
Let’s plot the kpoints
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(ebs.kpoints, color="blue", render_points_as_spheres=True)
p.show()
Other properties#
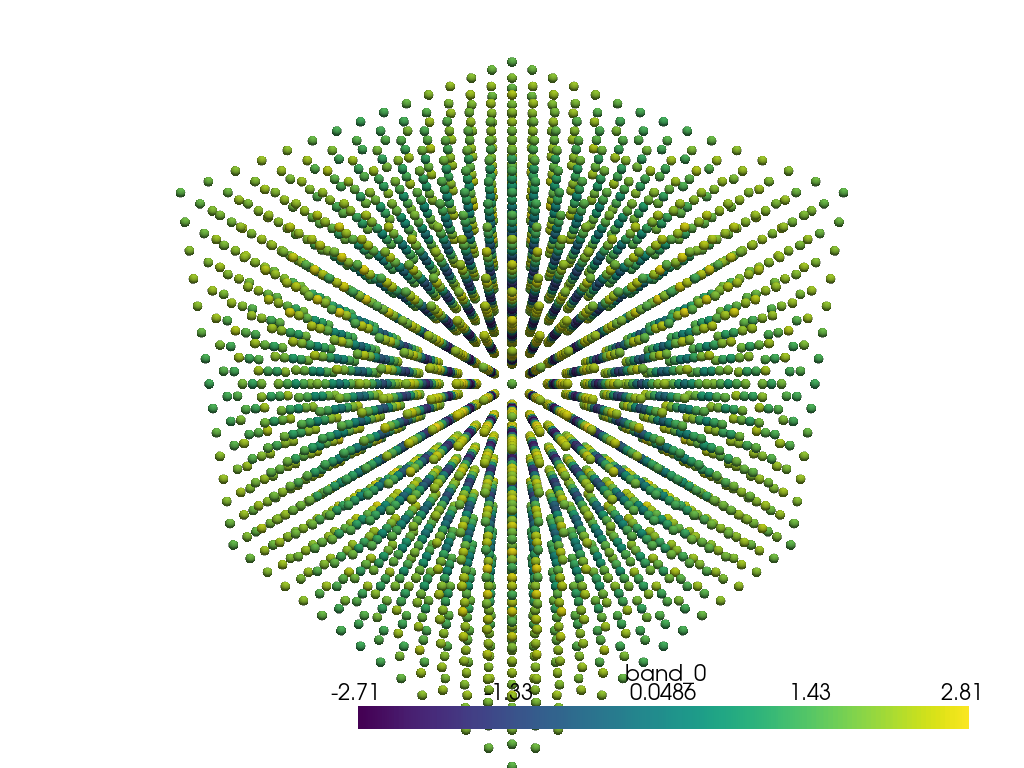
Bands#
kpoints = pv.PolyData(ebs.kpoints)
kpoints["band_0"] = ebs.bands[:, 0, 0]
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(
kpoints,
color="blue",
scalars="band_0",
render_points_as_spheres=True,
point_size=10,
)
p.show()
Projections#
print(f"Electron projected shape: {ebs.projected.shape}")
kpoints["band_0-atom_0-orbital_5-spin-0"] = ebs.projected[:, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0]
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(
kpoints,
color="blue",
scalars="band_0-atom_0-orbital_5-spin-0",
render_points_as_spheres=True,
point_size=10,
)
p.show()
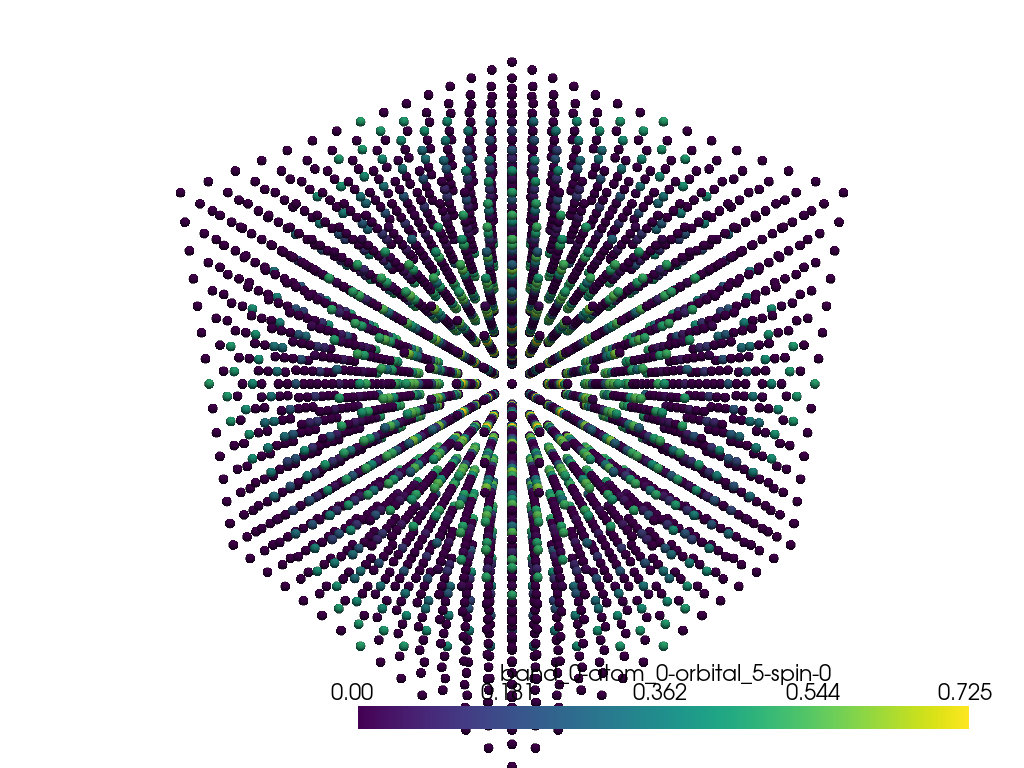
Electron projected shape: (3375, 8, 1, 1, 9, 1)
Gradients#
print(f"Band gradient shape: {ebs.bands_gradient.shape}")
kpoints["band_0-gradients"] = ebs.bands_gradient[:, 0, 0, :]
# Use the Glyph filter to generate arrows for the vectors
arrows = kpoints.glyph(orient="band_0-gradients", scale=False, factor=0.08)
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(arrows, scalar_bar_args={"title": "band_0-band_velocity"})
p.show()
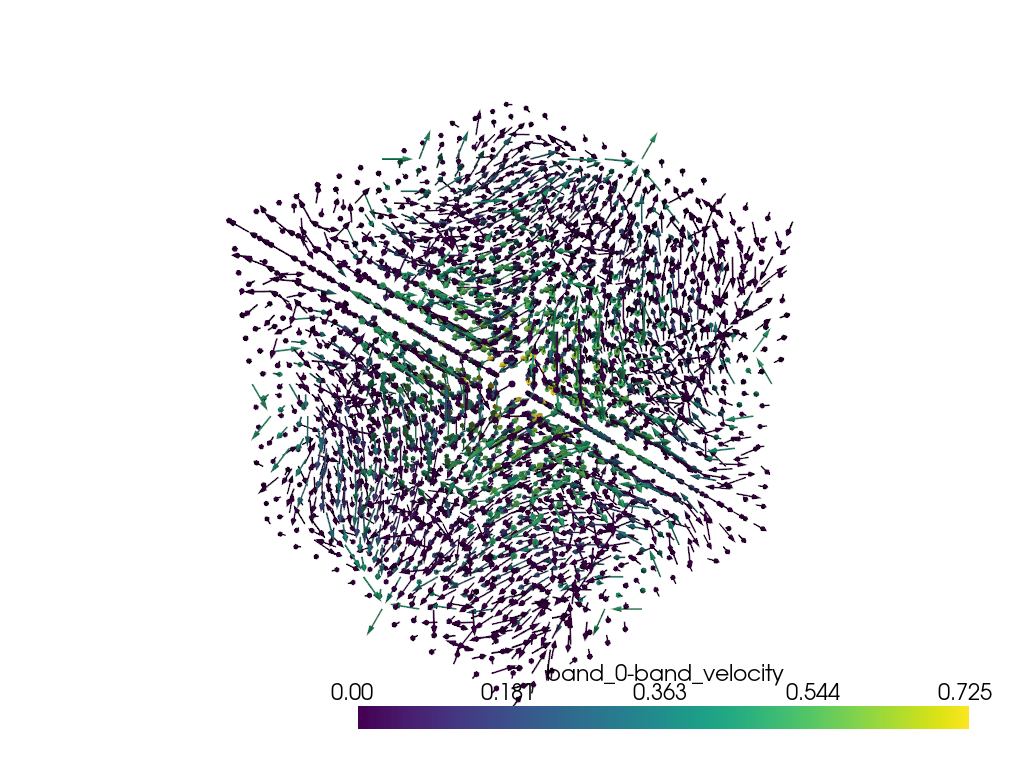
ij,uvwabj->uvwabi
Band gradient shape: (3375, 8, 1, 3)
Band/Fermi velocities#
print(f"Fermi velocity shape: {ebs.fermi_velocity.shape}")
print(f"Fermi speed shape: {ebs.fermi_speed.shape}")
kpoints["band_0-band_velocity"] = ebs.fermi_velocity[:, 0, 0, :]
kpoints["band_0-band_speed"] = ebs.fermi_speed[:, 0, 0]
arrows = kpoints.glyph(orient="band_0-band_velocity", scale=False, factor=0.08)
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(
kpoints,
scalars="band_0-band_speed",
render_points_as_spheres=True,
point_size=0.1,
show_scalar_bar=False,
)
p.add_mesh(arrows, scalar_bar_args={"title": "band_0-band_velocity"})
p.show()
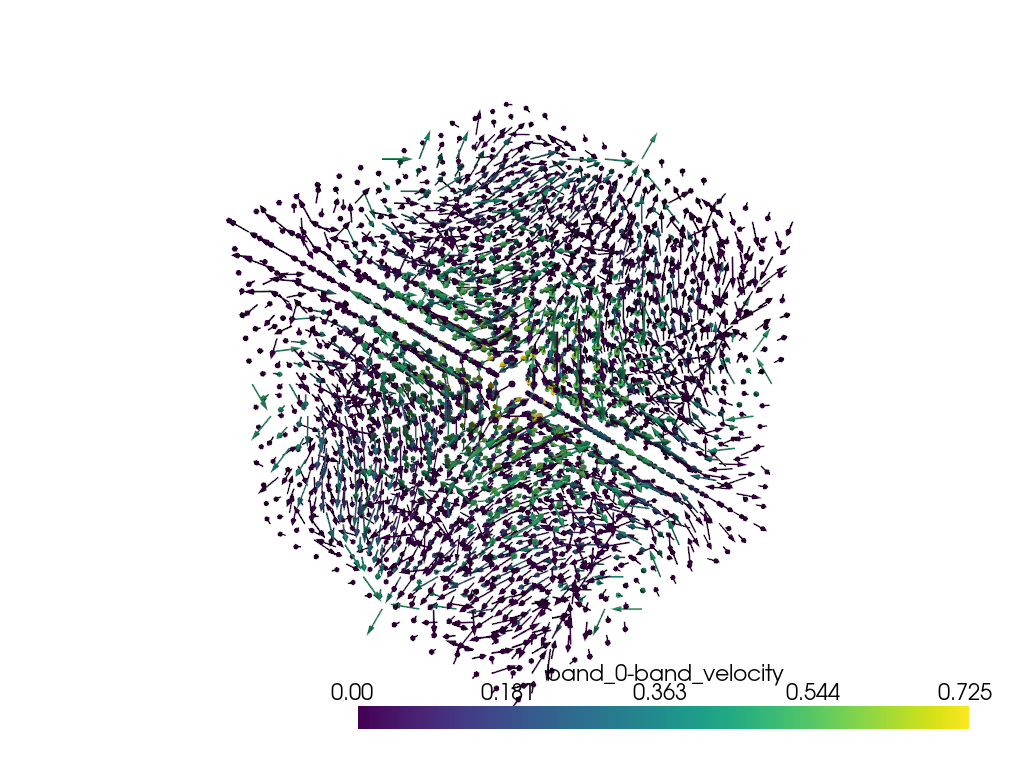
Fermi velocity shape: (3375, 8, 1, 3)
Fermi speed shape: (3375, 8, 1)
Effective mass#
print(
f"Harmonic average effective mass shape: {ebs.harmonic_average_effective_mass.shape}"
)
kpoints["band_0-harmonic_average_effective_mass"] = ebs.harmonic_average_effective_mass[
:, 0, 0
]
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(
kpoints,
scalars="band_0-harmonic_average_effective_mass",
render_points_as_spheres=True,
point_size=10,
)
p.show()
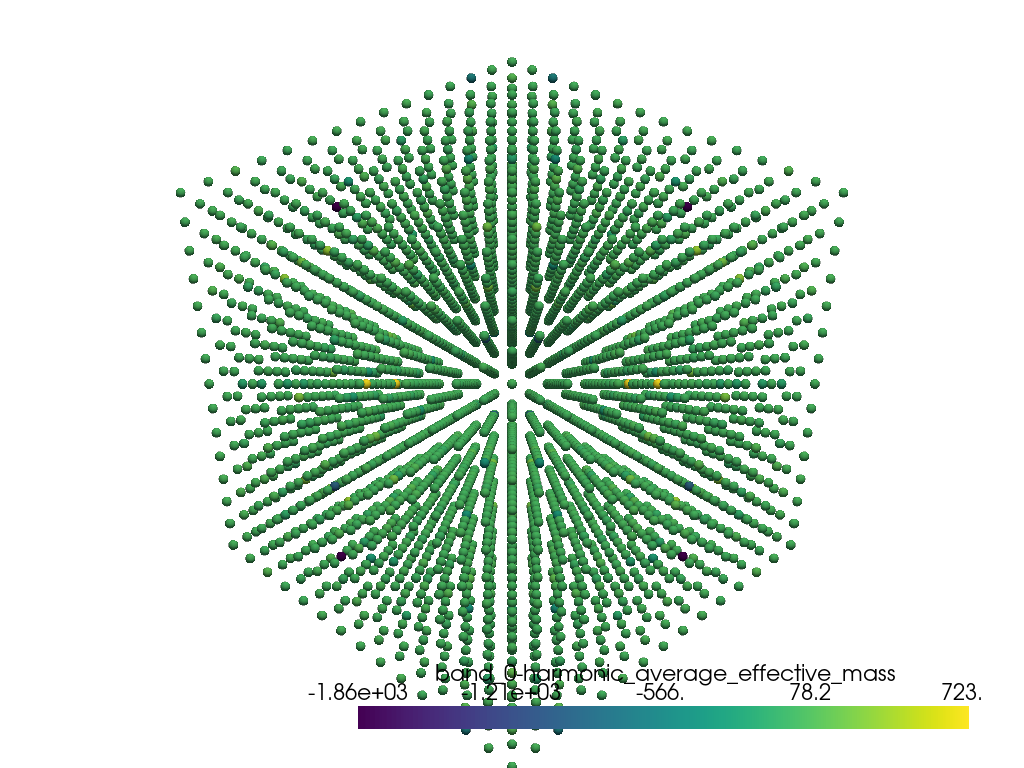
ij,uvwabcj->uvwabci
Harmonic average effective mass shape: (3375, 8, 1)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.069 seconds)